Dissertation: Putting Manufacturing in Cloud, to see the silver lining in digitalization and ...



“Cloud” is a metaphor for the Internet. Cloud computing means to provide virtualized computing resourcing and deliver hosted services over the Internet. It enables user to consume compute resources as a utility like electricity or water. It is a flexible way to increase capacity or add capabilities without investing in new physical infrastructure.
“Cloud computing is not only a change in technology, but also promises several attractive benefits for manufacturing industry”, says Hao who will defend her doctoral thesis at the University of Vaasa.
In the form of cloud manufacturing, a cooperative work environment is provided to all the companies in the entire manufacturing ecosystem. Instead of each company and factory being managed and monitored separately in the supply chain operations, manufacturers can establish a cloud enabled “system of collaborations”. This business model enables both internal and external communication and collaboration across multiple companies.
Hao explains that with the support of the cloud, manufacturers have the opportunity to manage their geographically distributed resources and provide manufacturing services to other factories regardless location.
“As manufacturers are work more closely with other parties and share more information with others, they become a virtual part of the manufacturer’s own organization”, says Hao.
Moreover, it is important to adapt the enterprise systems to the cloud, such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), MES (Machine Execution System), PPC (Production Planning and Control), RMA (Remote Monitoring Assistant). Hao says that this can ensure the movement of the entire manufacturing operations to “cloud”.
“By using these cloud-based systems, manufactures can quickly scale respond the business requirements, without massive IT costs, time and maintenance as before in on premise systems”.
The emergence of Internet of Things (IoT) and big data also change the manufacturing business model and stimulate the expansion of cloud manufacturing. More and more embedded devices, smart objects, and intelligent sensors are included in the manufacturing process to enable the communication both between manufacturers and the shop floor, and also between different partners. The real-time information about products, processes, and productions are acting as glue.
“The major original contribution of this work is its integration to the real manufacturing cases by four cases companies so that the actual industrial situation and concerns can be captured and reflected in the research”.
Hao also says, this research work is interesting and timely given because this concept is relatively new, and many companies are still struggling in transition of a new business model to face all the challenges in globalization.
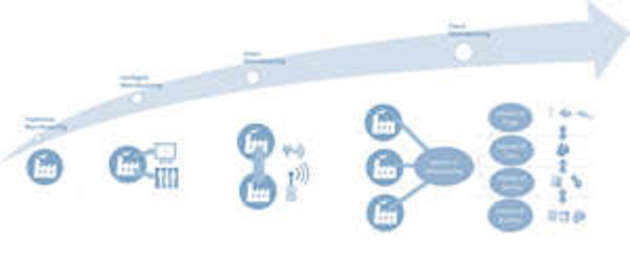
Figure: The figure shows the scope of cloud manufacturing and demonstrates how it is shifting from traditional manufacturing, to intelligent manufacturing, to smart manufacturing, and to today’s cloud manufacturing.

Further information
Yuqiuge Hao, tel +358 44 091 3928, yuqiuge.hao(at)uwasa.fi
Hao, Yuqiuge (2016) Cloud Manufacturing: Strategic Alignment between Manufacturing Industry and Cloud Computing. Acta Wasaensia 364, University of Vaasa
Publication pdf
Orders
Public Defense
The public examination of M.Sc. Yuqiuge Hao´s (Tech.) doctoral dissertation in the field of Industrial Management ”Cloud Manufacturing: Strategic Alignment between Manufacturing Industry and Cloud Computing” will be held on Friday, 9nd December 2016 at 12 o’clock in Auditorium Nissi (Tritonia).
Professor Jorge Pinho de Sousa (University of Porto) will act as an opponent and professor Petri Helo (University of Vaasa) as a custos. The examination will be held in English.
Attachments: